Overview
In a highly regulated industry, engineering automation companies must balance innovation with stringent compliance, standardized processes, and regulatory requirements. The Socioeconomic Kanban approach integrates software, hardware (IT/OT), and system requirements with operational and automated testing frameworks, ensuring organizational value, prioritization, cross-functionality, and improved collaboration.
In highly regulated industries, especially engineering automation, standardized processes are essential to ensure compliance, safety, and quality. The integration of IT and OT adds further complexity, as companies must align advanced IT systems with operational technologies, such as controllers and sensors. Strict compliance standards, combined with the need for operational efficiency, security, and adaptability, present challenges that must be navigated by balancing innovation with rigorous regulatory requirements.
Objectives
Key features include addressing internal bottlenecks, meeting deadlines, and aligning economic goals by focusing on primary objectives. The approach minimizes distractions, such as “micro-goal-frog,” leveraging requirement freezes to maintain focus and effectiveness.
Goals
- Organizational Value: Foster alignment with overarching priorities.
- Improved Collaboration: Promote cross-functionality and effective communication.
- Deadline Adherence: Ensure timely project delivery by addressing bottlenecks.
- Economic Focus: Prioritize primary goals, reducing scope creep and unnecessary delays.
A Component-Based Approach: A Fundamental Requirement for Development
Modularity: Components can be developed, tested, and validated independently, simplifying the management of complex interdependencies across departments (e.g., hardware, software, systems, and operations). This reduces complexity, enhances regulatory adherence, and fosters innovation across integrated departments.
Reducing Complexity with Socioeconomic Kanban
A component-based approach simplifies development by breaking down systems into manageable, modular parts. Socioeconomic Kanban supports this by:
- Time Management: Streamlining workflows and ensuring timely delivery.
- Artefact Handover: Creating clear, efficient handover mechanisms between departments.
- Requirement Freeze: Reducing scope creep and maintaining focus.
- Better Digitisation: Enhancing workflow visibility and collaboration across teams and departments.
Key Concepts to Meet Goals
To improve organizational agility and adaptability, we integrated key concepts mirroring strategies used in soccer:
- Adaptive Change Management: Just as soccer managers adjust strategies mid-game, businesses must adapt to market changes and emerging opportunities. Through Adaptive Change Management, we enable continuous evolution, ensuring organizations pivot swiftly and efficiently.
- Elasticity Mechanism: Just as soccer teams adjust tactics based on opponents, businesses can leverage elasticity to remain flexible in response to market shifts or disruptions. This ability to adjust is built into the workflow with clear, adaptive structures.
- Recovery Mechanism: Like soccer teams recalibrating after setbacks, businesses can swiftly recover from challenges. By setting up robust recovery mechanisms within the workflow, we ensure minimal disruption to overall performance.
- Variety: In soccer, variety maintains unpredictability and strength. Similarly, businesses must diversify workflows and offerings to cater to different customer needs. This approach reduces reliance on a single revenue stream, increasing operational resilience.
By integrating these concepts into the Socioeconomic Kanban approach, we create a systematic way of addressing interdependencies, improving cross-departmental collaboration, and accelerating decision-making speed. This comprehensive framework reduces bottlenecks, fosters proactive collaboration, and ensures that stakeholders stay aligned with both economic goals and regulatory compliance. These foundational principles create a smooth, efficient, and adaptable workflow, ensuring that all teams are aligned, aware of their responsibilities, and focused on delivering results promptly.

Optimising Cross-Departmental Collaboration for Streamlined Operations and Reduced Idle Time
- Set Cards for Involved Departments: Clearly define and document the responsibilities and contributions of each department involved. This helps identify when specific results need to be handed over to avoid idle time and keep workflows moving smoothly.
- Visualize Waiting Times: By tracking waiting times across departments, inefficiencies are highlighted, enabling faster decision-making and process acceleration.
- Collaborative Use Case Design: Promote interdepartmental collaboration to streamline operations and reduce silos, ensuring that teams work together toward shared goals, enhancing efficiency and project success.
- Milestone Focus: Use Socioeconomic Kanban as an interdependency interface to align departments on milestones.
- Digitized Checklists for Regulatory and Functional Requirements: Ensure clarity and consistency in meeting regulatory standards.
- Scaling Up or Down: Prioritize tasks on the Kanban board during regulatory audits or high-demand periods to optimize throughput.
- Adaptability and Cross-Functional Collaboration: Adapt product development to shifting priorities or regulatory updates.
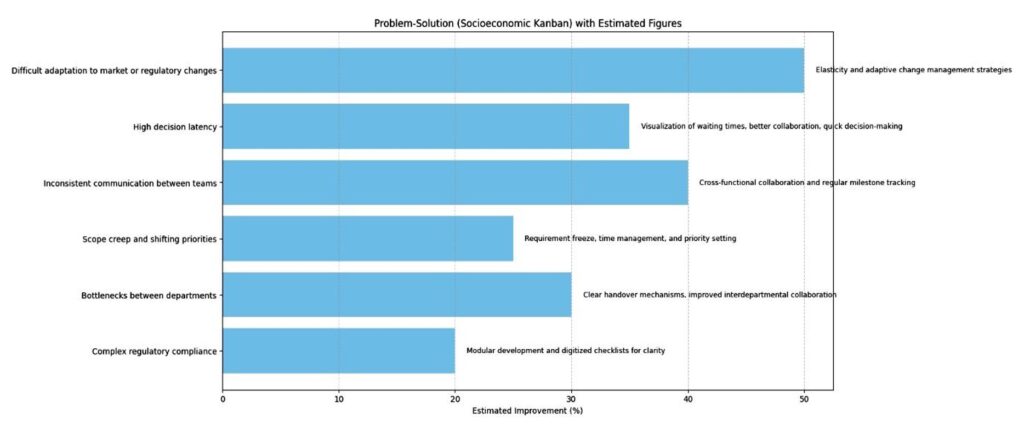
Key Takeaways
- The interventions or process changes are particularly effective in reducing requirements instability and improving operational rates.
- Smaller gains in resolving bottlenecks and delays highlight opportunities to target these areas for better efficiency in the future.
- Overall, this data provides a balanced overview of where progress has been made and where attention is still required to optimise processes further.
The chart highlights key organisational problems and their solutions, along with estimated improvements:
- Difficult adaptation to changes sees the highest improvement (50%) using adaptive change management strategies.
- High decision latency (35%) improves with visualisation, collaboration, and faster decisions.
- Inconsistent team communication (35%) benefits from cross-functional collaboration and milestone tracking.
- Other issues like scope creep, department bottlenecks, and regulatory compliance show 20-30% improvement through clearer processes, handovers, and checklists.
Summary
The Socioeconomic Kanban approach provides a flexible, scalable, and systematic way to manage the complexity of highly regulated engineering automation industries. By integrating modular development with effective time management, clear handovers, and focused collaboration, it reduces complexity and accelerates value creation. The key to success lies in fostering a collaborative culture across departments, leveraging strategic concepts like adaptive change management, elasticity, recovery mechanisms, and variety to meet evolving market and regulatory demands. The approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures that product development remain agile, compliant, and responsive in a competitive landscape.
Contact Us
We Shape The Future!
valuable. adaptive. innovative.
Our path of cooperation: Building trust, fostering relationships, and delivering value.
Get In Touch
- +43 664 5366975
- +43 3322 43215
- +381 65 6251 806
- [email protected]
Hours
- Mon-Fri 9:00AM - 5:00PM
- Sat 10:00AM - 2:00PM
